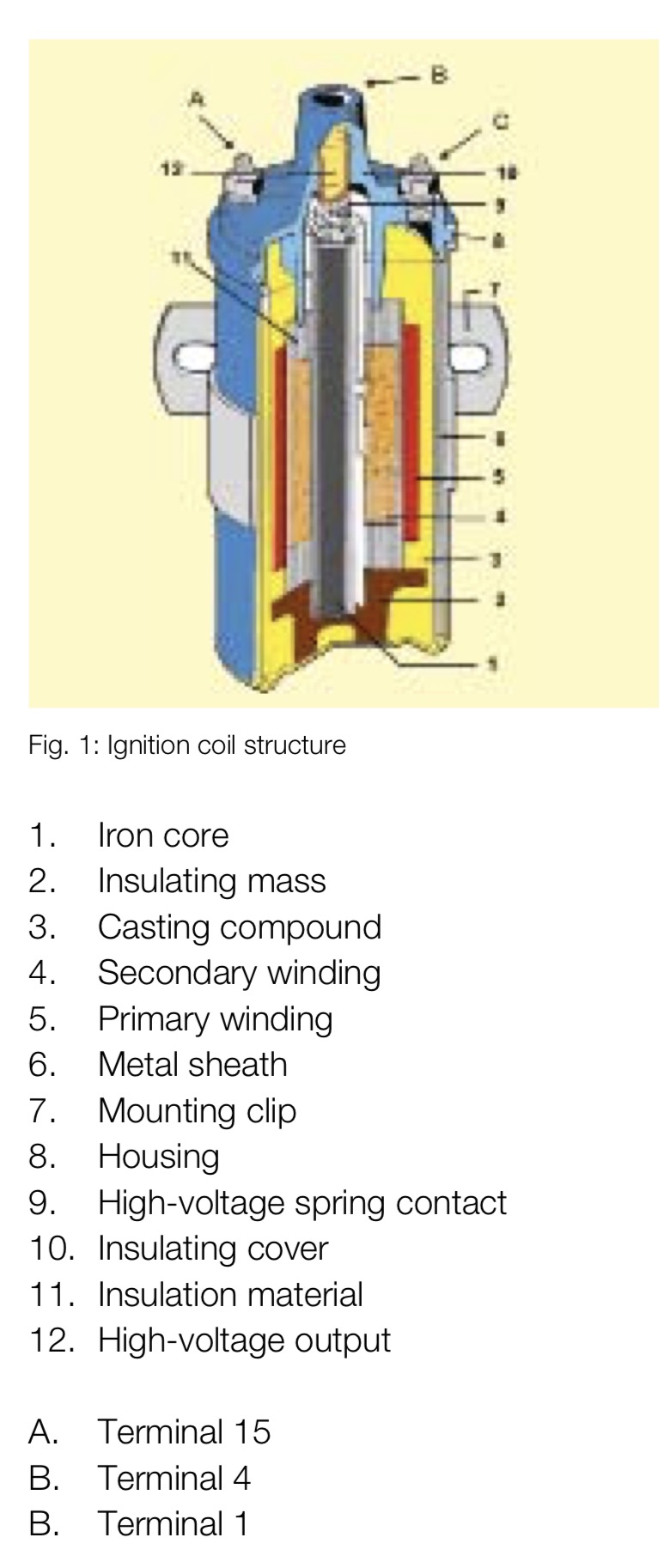
| Ignition Coils
|
|
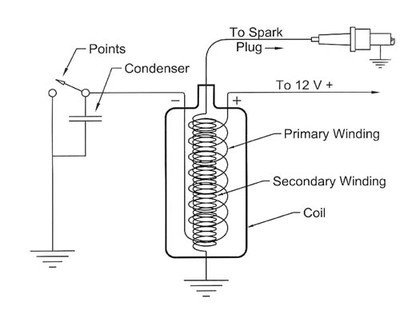
In typical use the coil is connected in series with a ballast resistor of a few ohms to reduce the voltage, which in turn reduces the current through the coil so it doesn't burn up. The ballast resistor isn't used during cranking (when the battery voltage is usually reduced to around 6-8 volts). A typical DC coil resistance would be around an ohm, and at 12 Volts, the DC current would be 12Amps, dissipating more than a 100 watts.
|
|
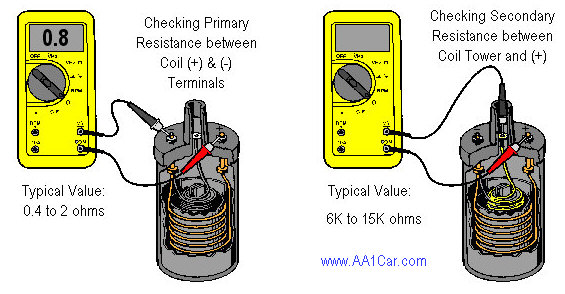
The primary coil should read between .4 ohms and 2.0 ohms, if outside this range replace it. The secondary coil should generally read between 7.5K ohms and 10.5K ohms.
In simple terms coils are rated by their primary resistance—less resistance in the primary windings of the coil allows more current to flow, which makes a stronger magnetic field. //// AND A HOTTER COIL ///// |

Primary resistance is measured with the probes on the positive and the negative terminals of the coil. MSD’s coils would be between .03 - .7 ohms |
| Delco 6-volt internal GM # 1115380 Delco 12-volt internal GM # 1115238 Delco 12-volt external GM# 1115202 Ford 6-volt external Ford # 8BA-12029 Ford 12-volt external Ford #D0RY-12029A Ford "blue top" internal for electronic ignition Ford # D5AZ-12029A Chrysler 6-volt firewall-mounted Chrysler # 862576 Chrysler 6-volt internal Chrysler #1300667 Chrysler 12-volt external Chrysler #2495531 Chrysler "tan top" external for electronic ignition Chrysler # 4176009
Putting 12 volt to the coil on start is a good thing. Putting constant 12 volt to the coil is a bad thing.
Avanti ignition resistor P/N 1550556 measures 0.6 Ohms The Avanti coil is Prestolite P/N 200607 service coil # P5-13. The listing for a R2 is Prestolite 200714 Service coil P5-57. The resistance of the coil in the Avanti and came up with 1.8 Ohms. With a 12 volt supply and a 0.6 resistor and a 1.8 ohm coil there would be 9 volts going to the coil and 3 volts dropped by the resistor. Recommended Coil/resistor for Stude V8 (all) Reference Red Bosch coil , and Mercedes' 1.8 ohm ballast resistor . (#0001581745). or
Red Bosch high performance coil, manufactured in Brazil, Part# 0221119030. |